|
|
|
Kamalpreet
|
Sustained Remission of Type-2 Diabetes on Plant-based Diet
|

|
|
|
|
Abstract
|
|
Type-2 diabetes (T2D) is a metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia. T2D may lead to health complications
such as retinal damage, chronic kidney disease, peripheral neuropathy, systemic hypertension, and coronary heart
disease. In the present case report, we observed remission of T2D in a newly diagnosed aged patient after initiation of a
customized nutritional intervention. The patient was able to achieve normal blood glucose readings without any
pharmacological treatment. HbA1c lowered from 13.30% to 5.60% after 12 months of nutritional intervention.
|
|
Keywords: Type-2 diabetes, Diabetes reversal, Plant-based diet.
|
|
|
|
Introduction
|
|
|
Diabetes is one of the most common metabolic disorders
that is associated with many life-threatening complications.
T2D is the most common type of diabetes worldwide. In
T2D, impaired receptors do not respond to insulin,
eventually leading to insulin resistance. A growing body of
evidence suggests that the rise in the consumption of ultra�processed food is associated with the rise in T2D around the
world1 . Patients typically are treated with glucose lowering
medications lifelong for long-term management of blood
glucose. Diet and lifestyle modification have been shown to
play a pivotal role in reversal of T2D by restoring the
glucose levels to normal range, potentially reducing, or
eliminating the requirement of medical therapy.
|
|
|
Glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) is considered a universally
accepted indicator of glycemic status. T2D remission is
defined as HbA1c levels of <6.5% over a period of three
months without any pharmacological treatment. In this case
report, we observed sustained remission of T2D after
initiation of a customized nutritional intervention without
administration of any pharmacological treatment.
|
|
|
Case presentation
|
|
|
We present a case of a 58-year-old female who was
diagnosed with T2D (HbA1c 13.30%) in Punjab, India in
May 2023. The patient complained of frequent urination,
increased thirst, unexplained weight loss, and excessive
fatigue. The doctor concerned prescribed metformin for
glucose control. She took the medications for a few weeks.
The patient was understandably hesitant to continue
pharmacological treatment and desired to reverse diabetes
through lifestyle change. She approached the author to assist
her in dietary modification.
|
|
|
Therapeutic intervention
|
|
|
The patient agreed to follow a customized nutritional
intervention for a period of 12 months. The prescribed diet was divided into breakfast, lunch, and dinner. Breakfast
included 500 to 600 grams of mixed fruit bowl. Lunch and
dinner included about 300 to 350 grams of raw vegetable
salad along with a cooked Indian meal each time. Total
snacks during the day included drinks like tender coconut
water and herbal tea besides a few soaked nuts or dates.
Ultra-processed food was strictly removed from the diet.
Processed dairy products and refined oil were removed from
the diet as these are associated with the increasing
prevalence of metabolic disorders2-4 . Blood glucose
readings of the patient were regularly monitored and
necessary changes in the diet were made as and when
required.
|
|
|
Results
|
|
|
The patient lowered her HbA1c from 13.30% to 5.60% after
12 months of customized nutritional intervention indicating
sustained remission of T2D. The patient was able to
eliminate the requirement of pharmacological therapy
within 2 weeks of nutritional intervention. The patient
continues to follow plant-based diet and does not require
medical intervention to maintain her healthy blood sugar
levels.
|
|
|
Discussion
|
|
|
Diet and lifestyle modification can play a major role in the
reversal of metabolic disorders like T2D. If left untreated,
T2D can lead to severe complications. T2D was believed to
be irreversible and progressive after diagnosis, but emerging
research suggests it can be reversed by following an
appropriate diet and lifestyle5-9 . In this case report, we
observed a stark difference in blood glucose readings before
and after following customized nutritional intervention in a
newly diagnosed T2D patient. Pre-intervention, the patient
had HbA1c of 13.30%. Post-intervention, she was able to
achieve an HbA1c of 5.60%. This case report on reversal of
T2D through dietary modification shall provide a ray of
hope to many T2D patients.
|
|
|
|
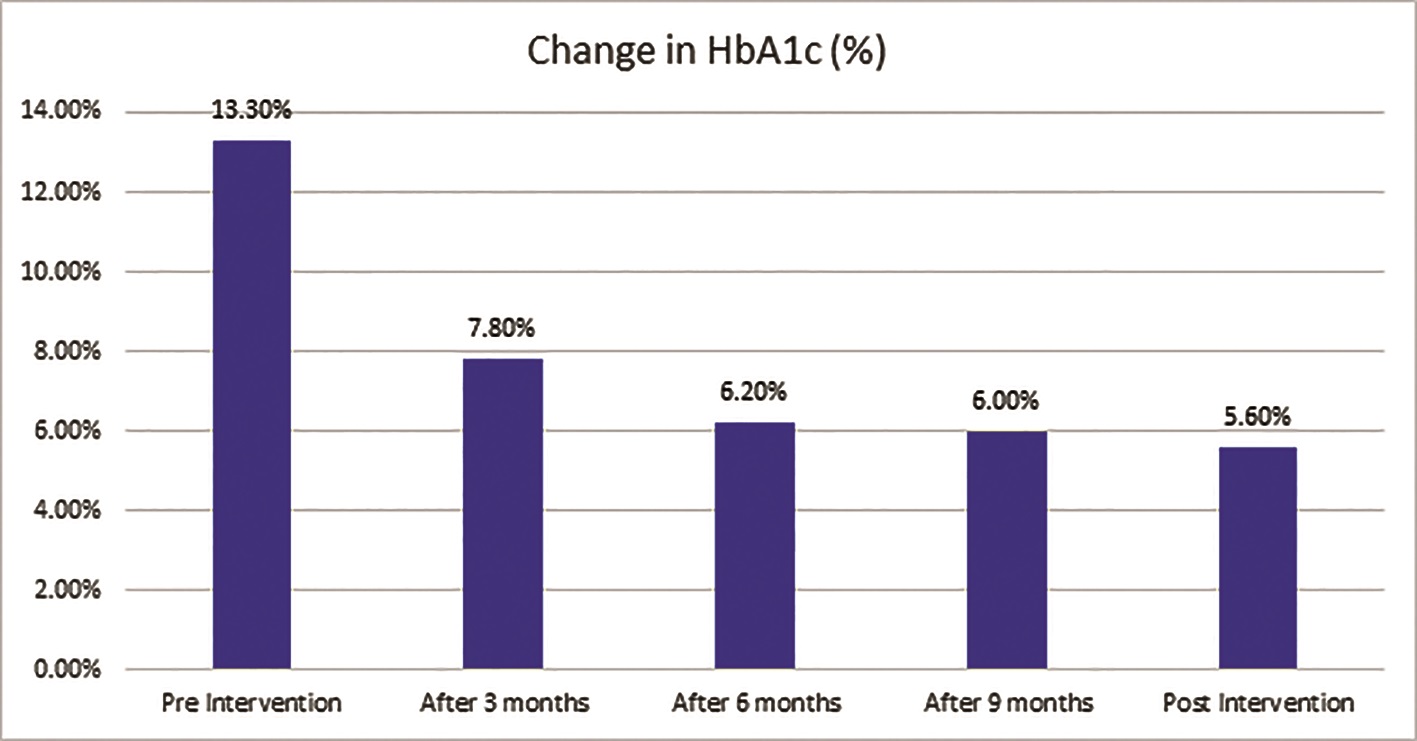
Figure 1: The graph shows HbA1c level of the patient during different phases of the
nutritional intervention.
|
|
|
Conclusion
|
|
|
Customized nutritional intervention helps in achieving sustained T2D remission, and it may be sustained in the
long-term. A randomized controlled trial with an adequate
sample size would support our observations.
|
|
|
|
References
|
|
1. Levy RB, Rauber F, Chang K, et al. Ultra-processed food
consumption and type 2 diabetes incidence: A prospective
cohort study. Clin Nutr. 2021 May; 40(5):3608-3614. doi:
10.1016/j.clnu.2020.12.018. Epub 2020 Dec 28. PMID:
33388205.
2. Esselstyn, Jr., C. B. (2019). Is Oil Healthy? International
Journal of Disease Reversal and Prevention.
https://doi.org/10.22230/ijdrp.2019v1n1a35
3. Gerstein HC. Cow's milk exposure and type I diabetes
mellitus. A critical overview of the clinical literature.
Diabetes Care ; 1994 Jan ; 17 (1) : 13 -9 . doi:
10.2337/diacare.17.1.13. PMID: 8112184.
4. Perez-Bravo F, Carrasco E, Gutierrez-Lopez MD, et al.
Genetic predisposition and environmental factors leading to
the development of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in
Chilean children. J Mol Med (Berl). 1996 Feb; 74(2):105-9.
doi: 10.1007/BF00196786. PMID: 8820406.
5. 5. Pramod Tripathi, Nidhi S. Kadam, Baby Sharma, et al.
Effectiveness of an intensive lifestyle modification program
on type 2 diabetes remission in Indian population. Diabetes
20 June 2023; 72 (Supplement_1): 1790–PUB.
https://doi.org/10.2337/db23-1790-PUB
6.Lim, E.L., Hollingsworth, K.G., Aribisala, B.S. et al.
Reversal of type 2 diabetes: Normalisation of beta cell
function in association with decreased pancreas and liver
triacylglycerol. Diabetologia 54, 2506–2514 (2011).
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-011-2204-7
7. Furmli S, Elmasry R, Ramos M, Fung J. Therapeutic use
of intermittent fasting for people with type 2 diabetes as an
alternative to insulin. BMJ Case Rep, 2018 Oct 9;
2018:bcr2017221854. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2017-221854.
PMID: 30301822; PMCID: PMC6194375
8. Kamalpreet Singh. Reversal of type 2 diabetes on a whole
food plant-based diet: A case report. International Journal
of Disease Reversal and Prevention, 2023, 5(2), 6 pp
https://doi.org/10.22230/ijdrp.2023v5n2a397
9. Kamalpreet Singh. Remission of type-2 diabetes on plant
based diet . Ayushdhara , 11 (2) , 71 -74 .
https://doi.org/10.47070/ayushdhara.v11i2.1502
|
|
Dr. Kamalpreet Singh
A3 Sukh Sehaj Enclave, Anandpur Sahib
Punjab, India - 140118
Ph: +919718422691
Email: coolkamal1997@gmail.com
Dr. Perla Sai Bhuvaneshwari
P.G. Scholar of Homoeopathic Materia Medica.
Bharati Vidyapeeth Homoeopathic Medical College,
Email: p.saibhuvana@gmail.com
Dr. Tejaswini Khachane
P.G. Scholar of Homoeopathic Materia Medica.
Bharati Vidyapeeth Homoeopathic Medical College,
Katraj, Dhankawadi, Pune, India - 411043.
Email: khachanetejaswini@gmail.com
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Updates
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|